THM | The Lay of the Land

Red Teaming | The Lay of the Land | Summary:
This room offers hands-on learning about corporate security technologies. It covers Active Directory (AD) management, host solutions like antivirus, firewalls, Sysmon, HIDS/HIPS, EDR, network security with firewalls, SIEM, and IDS/IPS, plus applications and services including installed programs, processes, file sharing, DNS, local apps.
More importantly, it equips learners with practical knowledge of corporate security infrastructures.
Please note that this write-up is NOT intended to replace the original room or its content, but rather serve as supplementary material for those who are stuck and need additional guidance. This walkthrough provides one (of the many) possible solution to the challenges, without revealing any flags or passwords directly.
01 | Introduction
In red team engagement, establishing a clear understanding of the compromised machine's environment is crucial. This involves conducting extensive reconnaissance and enumeration to gather critical information.
The process begins with obtaining initial access, followed by post-exploitation activities aimed at learning about the network infrastructure, active directory structure, user and group access permissions, host-based security tools, network-based security solutions, and operational applications/services.
This comprehensive approach helps red teams map out potential attack vectors, mimic real-world adversary behaviors, and strategically exploit weaknesses. The goal is to create a detailed environment model, facilitating informed decision-making for subsequent phases of engagement.
Question 1: Let's start learning!
No answer needed
02 | Deploy the VM
| RDP Access | Credentials |
|---|---|
| username | kkidd |
| password | Pass123321@ |
My choice of RDP connection:
xfreerdp3 /u:"kkidd" /p:"Pass123321@" /v:<targetbox-ip> /dynamic-resolution /compression /network:auto /gfx:AVC420:on +clipboard -themes
Question 1: Let's discuss the common network infrastructure in the next task!
No answer needed
03 | Network Infrastructure
During a red team engagement on an unknown network, the primary objective upon gaining initial access is to determine the specific target system, its service function, and the overall network environment. This process involves meticulous enumeration of the compromised machine to gather essential information about its configuration, services, and connections.
- Network Segmentation | a security measure that divides a network into multiple subnets, enhancing both security and management
- It aims to safeguard sensitive data like customer records and financial information from unauthorized access
- VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) | to address issues such as broadcast storms and improve overall security
- Within a VLAN, hosts can only communicate with others within the same network segment.
- Internal Networks
- segmented based on device importance or data accessibility
- implement segmentation to manage traffic, enhance performance, and bolster security
- DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
- Acts as a buffer zone between the internal network and the public internet
- Protects internal assets from direct internet access while allowing necessary traffic
- Network Enumeration
- checking TCP and UDP ports, established connections, routing tables, ARP tables
- example |
netstatnetstat \?
# Displays protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections.
# -n: Displays addresses and port numbers in numerical form.
# -a: Displays all connections and listening ports.
netstat -na
# -r: Displays the routing table.
# -b: Displays the executable involved in creating each connection or listening port. (requires high level privileges) - example |
arp# Displays and modifies the IP-to-Physical address translation tables used by address resolution protocol (ARP).
# help
arp
# -a: Displays current ARP entries by interrogating the current protocol data
arp -a
# -v: Displays current ARP entries in verbose mode. All invalid entries and entries on the loop-back interface will be shown.
arp -a -v
Question 1: Read the above!
No answer needed
04 | Active Directory (AD) environment
Active Directory (AD) is a Windows-based directory service that centralizes user management, authentication, and authorization within a network. It organizes and manages network resources such as users, computers, printers, and more, providing essential information like job titles, contact details, passwords, and permissions.
- Domain Controllers | a Windows server that provides Active Directory services and controls the entire domain
- centralized servers managing the domain, responsible for encryption, access control, resource sharing, and containing high-value data.
- Organizational Units (OUs) | Hierarchical containers within domains for organizing users and resources.
- Active Directory Objects | Include users, groups, and hardware components like computers and printers. Domains maintain databases with object information.
Quote | Active Directory Object Examples
- Users | "A security principal that is allowed to authenticate to machines in the domain"
- Computers | "A special type of user accounts"
- GPOs | "Collections of policies that are applied to other AD objects"
- AD Domains | Collections of AD components, with a forest being a group of interconnected domains.
- Service Accounts | Types include built-in local users, Domain users, and Managed service accounts.
- Domain Administrators | Manage domain settings and policies.
- AD Forest | a collection of domains that trust each other
Knowing the AD environment is crucial for red teamers. By enumerating AD structures, they gain access to detailed information, facilitating lateral movement within networks during attacks.
Check if a Computer is part of an AD Domain | systeminfo | findstr Domain
"Note that if we get WORKGROUP in the domain section, then it means that this machine is part of a local workgroup."
Q & A
Use systeminfo | findstr Domain on the target to answer the following two questions.
Question 1: Before going any further, ensure the attached machine is deployed and try what we discussed. Is the attached machine part of the AD environment? (Y|N)
Y
Question 2: If it is part of an AD environment, what is the domain name of the AD?
thmredteam.com
05 | Users and Groups Management
Understanding the Active Directory (AD) environment is crucial once initial access to a compromised machine is achieved. This process involves identifying various types of AD service accounts and leveraging enumeration techniques to gather essential information.
AD Service Accounts
- Note | Common Active Directory Service Accounts
- Built-in Local Users | These are used for local system management and exist outside the AD environment.
- Domain User Accounts | Provide access to AD services, managed by domain administrators.
- Managed Service Accounts | Limited domain user accounts with higher privileges for managing AD services.
- Domain Administrators | user accounts that can manage information in an Active Directory environment
- manage information like | AD configurations | users | groups | permissions | roles | services
AD Administrator Accounts
- BUILTIN\Administrator | Local admin access on a domain controller
- Domain Admins | Administrative access to all resources in the domain
- Enterprise Admins | Available only in the forest root
- Schema Admins | Capable of modifying domain/forest; useful for red teamers
- Server Operators | manage domain servers
- Account Operators | manage users that are not in privileged groups
AD Enumeration
"The Distinguished Name (DN) is a collection of comma-separated key and value pairs used to identify unique records within the directory. The DN consists of Domain Component (DC), OrganizationalUnitName (OU), Common Name (CN), and others."
"The following "CN=User1,CN=Users,DC=thmredteam,DC=com" is an example of DN, which can be visualized as follow:"
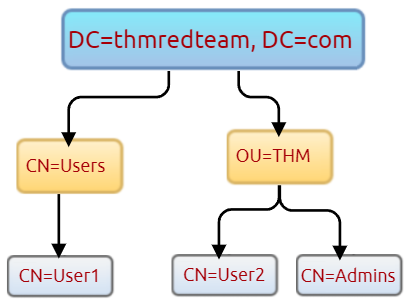
# Retrieve all active directory user accounts within the current domain
Get-ADUser -Filter *
# specify a ***Common-Name (CN)*** and list users that are part of `Users`
Get-ADUser -Filter * -SearchBase "CN=Users,DC=THMREDTEAM,DC=COM"
#specify a `OU` and list users that are part of `THM`
Get-ADUser -Filter * -SearchBase "OU=THM,DC=THMREDTEAM,DC=COM"
Q & A
Simply run Get-ADUser -Filter * -SearchBase "OU=THM,DC=THMREDTEAM,DC=COM" in powershell to answer the next two questions.
Question 1: Use the Get-ADUser -Filter * -SearchBase command to list the available user accounts within THM OU in the thmredteam.com domain. How many users are available?
6
Question 2: Once you run the previous command, what is the UserPrincipalName (email) of the admin account?
06 | Host Security Solution - 1
Antivirus Software (AV)
- General
- is designed to detect, monitor, and prevent malicious software by scanning files and systems
- regular updates are necessary as the software relies on virus definitions, which are matched against known signatures
- Key Features
- Background Scanning | antivirus software works in real-time and scans all open and used files in the background
- Full System Scan | scan the whole system
- Virus Definitions | where it replies to the pre-defined virus
- Detection Techniques
- Signature-based | Uses a database of known malicious signatures to identify threats
- Heuristic-based | Utilizes machine learning to analyze code or API usage in real-time
- Behavior-based | Monitors for abnormal activities like registry changes or process modifications
- Enumerating AV software
- Note | Win. Servers may not have
SecurityCenter2namespace > works in Win. Workstations - wmic |
wmic /namespace:\\root\securitycenter2 path antivirusproduct - powershell |
Get-CimInstance -Namespace root/SecurityCenter2 -ClassName AntivirusProduct
- Note | Win. Servers may not have
Microsoft Windows Defender
- General
- pre-installed antivirus tool designed to protect endpoints
- it employs advanced algorithms, including machine learning and big-data analysis, to detect and combat malware and viruses
- Protection Modes
- Active Mode | default setting where it functions as the primary antivirus, offering real-time protection and remediation
- Passive Mode | used when a third-party antivirus is installed, acting as a secondary tool that scans files but does not remove threats (no remediation!)
- Disable Mode | disabled or removed from the system, preventing its operation
- Enumerating Defender
Get-Service WinDefend| check the service stateGet-MpComputerStatus | select RealTimeProtectionEnabled| check if Defender is enabled or not- without specifying, it provides the current status of all security solution elements
Host-based Firewall
- General
- a security tool installed on a machine designed to protect it by controlling inbound and outbound network traffic
- acts as a gatekeeper, allowing only trusted devices on the same network while blocking unauthorized access
- is crucial for preventing unauthorized access
- Key Features
- can monitor and manage network traffic at the network layer
- can block malicious or untrusted packets, such as ICMP requests in a
pingcommand - can inspecting higher OSI layers (e.g., application layer) to detect and block attacks like SQL injection
- Enumerating Firewall Settings
# check the profile settings
Get-NetFirewallProfile | Format-Table Name, Enabled
# disabling firewall profiles | Requires admin privileges
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Profile Domain, Public, Private -Enabled False
# check firewall rules
Get-NetFirewallRule | select DisplayName, Enabled, Description
# to check and verify what exactly the firewall blocks > `Test-NetConnection` | `TcpClient`
# test inbound connection without extra tools
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName 127.0.0.1 -Port 80
Q & A
Question 1: Enumerate the attached Windows machine and check whether the host-based firewall is enabled or not! (Y|N)
N
Check out which of the firewall profiles are enabled. It seems like none of them is.
PS C:\Users\kkidd> Get-NetFirewallProfile | format-table name, enabled
name Enabled
---- -------
Domain False
Private False
Public False
PS C:\Users\kkidd>
Question 2: Using PowerShell cmdlets such Get-MpThreat can provide us with threats details that have been detected using MS Defender. Run it and answer the following: What is the file name that causes this alert to record?
PowerView.ps1
Check it with Get-MpThreat.
PS C:\Users\kkidd> Get-MpThreat
...<OMITTED-FOR-BREVITY>...
CategoryID : 34
...<OMITTED-FOR-BREVITY>...
Resources : {file:_C:\Users\kkidd\Desktop\PowerView.ps1,
containerfile:_C:\Users\kkidd\Desktop\PowerView.ps1,
file:_C:\Users\kkidd\Desktop\PowerView.ps1->(UTF-8)}
RollupStatus : 1
...<OMITTED-FOR-BREVITY>...
Question 3: Enumerate the firewall rules of the attached Windows machine. What is the port that is allowed under the THM-Connection rule?
17337
Check all the firewall rules and filter for the THM-Connection string.
PS C:\Users\kkidd> Get-NetFirewallRule | findstr "THM-Connection"
DisplayName : THM-Connection
Description : THM-Connection inbound to 17337 Port!
PS C:\Users\kkidd>
Question 4: In the next task, we will keep discussing the host security solution. I'm ready!
No answer needed
07 | Host Security Solution - 2
Security Event Logging and Monitoring
- General | are crucial tools for system administrators and security teams to monitor and analyze activities within a network or on individual machines
- Windows operating systems log events categorized by types such as application, system, security, and services
- these logs help identify installed components like Active Directory and DNS servers
- in corporate settings, log agent software is employed to collect logs from various sensors, aiding network monitoring and incident analysis
- Enumerating EventLogs |
Get-EventLogGet-EventLog -List| check the available event log categories- Get-Eventlog | Official Documentation
System Monitor (Sysmon)
- General | a tool from Microsoft’s Sysinternals suite, is not installed by default but can be started to log various system events
- these logs are valuable for system administrators and security teams (blue teamers) in detecting malicious activities and aiding in troubleshooting
- Key Features
- monitors processes, network connections, file modifications, remote threats, process and memory access, etc.
- allows custom rule creation for specific monitoring needs
- Enumerating Sysmon
# check for processes named *"Sysmon"*
Get-Process | Where-Object { $_.ProcessName -eq "Sysmon" }
# check for services referencing *"sysmon"*
Get-CimInstance win32_service -Filter "Description = 'System Monitor service'"
# check for services referencing *"sysmon"*
Get-Service | where-object {$_.DisplayName -like "*sysm*"}
# check the windows registry
reg query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WINEVT\Channels\Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational - if installed and operational > check out it's configuration to understand more
# look for it's config file
# example was located at "c:\tools\sysmon\symonconfig.xml"
findstr /si '<ProcessCreate onmatch="exclude">' C:\tools\*
HIDS | HIPS
- General | Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) are software tools designed to monitor and detect suspicious activities on a host computer
- Operation Methods
- Signature-based Detection | identifies threats by matching known signatures using checksums and message authentication
- Anomaly-based Detection | flags unusual behaviors, such as abnormal bandwidth usage, protocols, or ports
- General | Host-based Intrusion Prevention Systems (HIPS) extend this functionality by preventing malicious activities through features like:
- Auditing log files | Monitoring processes | Protecting system resources
- Combining tools such as antivirus, behavior analysis, network protection, and application firewalls
EDR
Scripts like Invoke-EDRChecker and SharpEDRChecker help enumerate security products on a machine by examining file metadata, processes, DLLs, services, and drivers.
- General | Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is an advanced cybersecurity solution designed to detect and respond to malicious activities on individual endpoints
- it monitors for threats such as malware, exploit chains, and ransomware in real-time, providing detailed analytics for investigation and response
- provides comprehensive endpoint protection by combining threat detection with response capabilities to safeguard against evolving cyber threats
- Popular EDR solutions
- Cylance, CrowdStrike, Symantec, SentinelOne
Even if an attacker bypasses initial detection, EDR continues to monitor and can block actions upon detecting anomalies.
Question 1: We covered some of the common security endpoints we may encounter during the red team engagement. Let's discuss the network-based security solutions in the next task!
No answer needed
08 | Network Security Solutions
Network Firewall
- General
- a critical security component that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined rules and policies
- acts as the first line of defense against untrusted external traffic, ensuring only authorized access is granted to a network or specific applications
- modern firewalls are often integrated into network routers or security appliances, offering robust features that enhance network security and data protection
- Key Types of Firewalls
- Packet-filtering firewalls | these inspect traffic at the network layer, allowing or blocking packets based on criteria such as source IP address
- Proxy firewalls | Function as intermediaries, managing network traffic between trusted internal networks and external sources by providing security services like authentication and encryption
- NAT firewalls | Combine network address translation with firewall capabilities to hide internal IP addresses and control access while translating private IPs to public ones
- Web application firewalls (WAFs) | Protect web applications from cyber threats by analyzing traffic and enforcing rules based on application logic, mitigating risks like SQL injection and XSS
SIEM
- General | Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- an integral solution that combines Security Information Management (SIM) and Security Event Management (SEM) to enable real-time monitoring, analysis, and response to security events
- helps organizations proactively identify and mitigate potential threats by aggregating log data from various network sources and applying advanced analytics to detect unusual patterns or behaviors
- SIEM systems are capable of addressing a wide range of threats, including Insider Threats, security vulnerabilities, phishing attacks, web-based threats, DDoS attacks, and data exfiltration
- Key Functions
- Log Management | centralized collection of logs from across the network for comprehensive monitoring
- Event Analytics | utilizes AI and threat intelligence to detect abnormal activities, enabling timely incident response
- Incident Monitoring and Alerts | notifications for potential threats, allowing administrators to take action before damage occurs
- Compliance Reporting | generates real-time reports to aid in decision-making and ensure regulatory compliance
- Popular SIEM tools
- Splunk | LogRhythm NextGen SIEM Platform | SolarWinds Security Event Manager | Datadog Security Monitoring
IDS | IPS
Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (NIPS) are network security solutions designed to monitor and protect enterprise networks from cyber threats. Both systems analyze network traffic for suspicious activities or known malicious patterns.
-
IDS | Focuses on detecting potential intrusions by monitoring network packets for anomalies
- it alerts administrators, who then need to manually intervene or use additional tools to address the threat
-
IPS | Enhances IDS functionality by automatically blocking or rejecting packets deemed suspicious based on predefined policies and rules, preventing potential breaches
-
Common enterprise solutions
- Palo Alto Networks
- Cisco's Next-Generation Security System
- McAfee Network Security Platform (NSP)
- Trend Micro TippingPoint
- Suricata
These systems play a crucial role in network security by providing real-time threat detection and response capabilities.
Question 1: Read the above!
No answer needed
09 | Applications and Services
Installed Applications
- General | Enumerating a system's installed applications involves identifying software by name and version
- Goal | to identify potentially vulnerable software that can be exploited to gain unauthorized access or escalate privileges
- this enumeration may reveal plain-text credentials, which could belong to other systems or services
- Enumerating Installed Applications
wmic product get name,version| list all installed applications and their versionsGet-ChildItem -Hidden -Path C:\Users\kkidd\Desktop\| look for hidden directories
Services and Process
-
General
- Enumerating running services and processes on a target system is a critical step and involves identifying software executables and their configurations to uncover potential vulnerabilities, especially misconfigured permissions that may escalate user access levels.
-
Key objectives
- Identifying Running Services | To detect Windows services and applications running within their own sessions
- Discovering Misconfigured Permissions | To identify vulnerabilities in service configurations that could be exploited
- Gathering Process Information | To gather details about custom-developed applications or sensitive information associated with running processes
-
Enumerating Services and Processes
# list running services (started)
net start
# get more info about a particular service (here:'THM Demo')
# example service path: c:\windows\thm-demo.exe
wmic service where "name like 'THM Demo'" get Name,PathName
# once the process is identified > check the process
# will provide us with the process id (here:3212)
Get-Process -Name thm-demo
# check for listening ports by that process id
netstat -noa |findstr "LISTENING" |findstr "3212"
This enumeration helps in understanding the system's configuration, revealing potential escalation vectors and areas for further investigation.
Sharing files and Printers
- you might find some misconfigured access permissions and some useful information about other accounts and systems
Internal services | DNS | local web applications | etc
- Common Internal Services
- DNS Services | Email Services | Network File Share | Web application | Database service
Q & A
Question 1: Finally, we can see it is listening on port 8080. Now try to apply what we discussed and find the port number for THM Service. What is the port number?
13337
So, in a nutshell, check the started services, identify the interesting service and get more information about it. Then check out the identified process and check for listening ports associated with it's PID.
Here is the whole terminal interaction shortened for brevity.
PS C:\Users\kkidd> net start
These Windows services are started:
Active Directory Web Services
...<OMITTED-FOR-BREVITY>...
Themes
THM Service
Time Broker
...<OMITTED-FOR-BREVITY>...
The command completed successfully.
PS C:\Users\kkidd> wmic service where "name like 'THM Service'" get Name,PathName
Name PathName
THM Service c:\Windows\thm-service.exe
PS C:\Users\kkidd> Get-Process -name thm-service
Handles NPM(K) PM(K) WS(K) CPU(s) Id SI ProcessName
------- ------ ----- ----- ------ -- -- -----------
78 9 12668 5612 2784 0 thm-service
PS C:\Users\kkidd> netstat -noa | findstr "LISTENING" | findstr "2784"
TCP 0.0.0.0:13337 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 2784
TCP [::]:13337 [::]:0 LISTENING 2784
PS C:\Users\kkidd>
Question 2: Visit the localhost on the port you found in Question #1. What is the flag?
<flag>
Use curl to grab the flag.
PS C:\Users\kkidd> curl http://localhost:13337
StatusCode : 200
StatusDescription : OK
Content : Hi the flag is: THM{<flag>}
RawContent : HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 44
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
Date: <date>
Hi the flag is: THM{<flag>}
Forms : {}
Headers : {[Content-Length, 44], [Content-Type, text/plain;
charset=utf-8], [<date>]}
Images : {}
InputFields : {}
Links : {}
ParsedHtml : System.__ComObject
RawContentLength : 44
PS C:\Users\kkidd>
Question 3: Now enumerate the domain name of the domain controller, thmredteam.com, using the nslookup.exe, and perform a DNS zone transfer. What is the flag for one of the records?
<flag>
-
Step-1 | Run
nslookup.exe -
Step-2 | Specify the DNS Server to query and set it to our targetbox
server NAME| set default server to NAME, using current default server- in our case |
server <targetbox-ip
-
Step-3 | Try the DNS zone transfer on the domain that we found in AD |
ls -d thmredteam.comls| list addresses in DOMAIN-d| list all records
-
Step-4 | Grab the flag from the records.
Here is the whole terminal interaction.
PS C:\Users\kkidd> nslookup.exe
Default Server: ip-10-0-0-2.eu-west-1.compute.internal
Address: 10.0.0.2
> server 10.10.229.147
Default Server: ip-10-10-229-147.eu-west-1.compute.internal
Address: 10.10.229.147
> ls -d thmredteam.com
[ip-10-10-229-147.eu-west-1.compute.internal]
thmredteam.com. SOA ad.thmredteam.com hostmaster.thmredteam.com. (749 900 600 86400 3600)
thmredteam.com. A 10.10.129.59
thmredteam.com. NS ad.thmredteam.com
_msdcs NS ad.thmredteam.com
_gc._tcp.Default-First-Site-Name._sites SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=3268, ad.thmredteam.com
_kerberos._tcp.Default-First-Site-Name._sites SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=88, ad.thmredteam.com
_ldap._tcp.Default-First-Site-Name._sites SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=389, ad.thmredteam.com
_gc._tcp SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=3268, ad.thmredteam.com
_kerberos._tcp SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=88, ad.thmredteam.com
_kpasswd._tcp SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=464, ad.thmredteam.com
_ldap._tcp SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=389, ad.thmredteam.com
_kerberos._udp SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=88, ad.thmredteam.com
_kpasswd._udp SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=464, ad.thmredteam.com
ad A 10.10.229.147
DomainDnsZones A 10.10.129.59
_ldap._tcp.Default-First-Site-Name._sites.DomainDnsZones SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=389, ad.thmredteam.com
_ldap._tcp.DomainDnsZones SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=389, ad.thmredteam.com
flag TXT "THM{<flag>}"
ForestDnsZones A 10.10.129.59
_ldap._tcp.Default-First-Site-Name._sites.ForestDnsZones SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=389, ad.thmredteam.com
_ldap._tcp.ForestDnsZones SRV priority=0, weight=100, port=389, ad.thmredteam.com
www A 10.10.141.51
thmredteam.com. SOA ad.thmredteam.com hostmaster.thmredteam.com. (749 900 600 86400 3600)
>
10 | Conclusion
Question 1: Hope you enjoyed the room and keep learning!
No answer needed